The Vitamins and Minerals That Support Energy Indirectly
In the previous blog, we explored the vitamins and minerals that directly participate in ATP production, which is the process
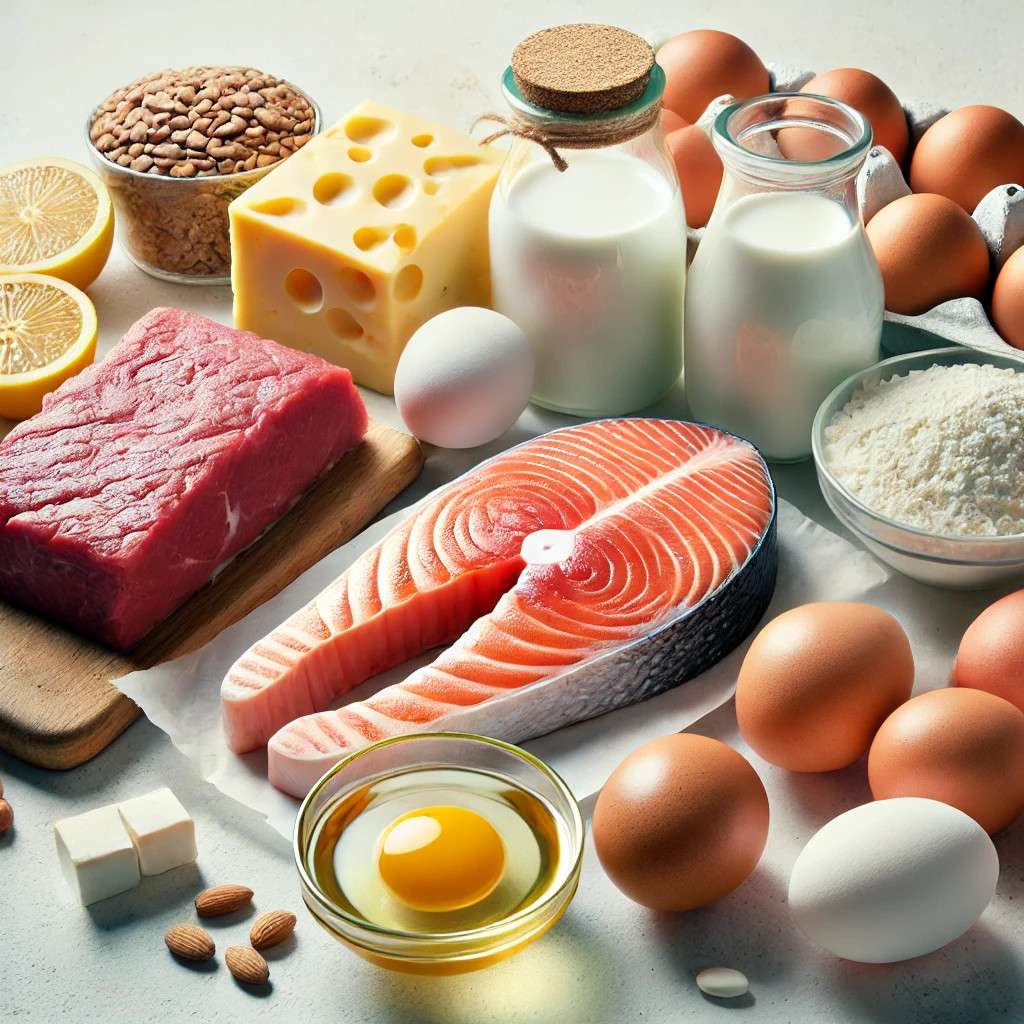

B12 absorption occurs in two ways: active absorption and passive diffusion.
This means that for individuals with absorption issues, a high-dose B12 supplement ensures that enough gets into the body through passive diffusion, even if the active absorption pathway is compromised.
While the absorption of synthetic (crystalline) B12 from supplements remains relatively stable, the absorption of natural food-bound B12 decreases significantly in older adults. This decline is largely due to atrophic gastritis, a condition that reduces stomach acid production, impairing the release of B12 from proteins in food.
A study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition highlights that as many as 10-30% of older adults may struggle to absorb B12 from dietary sources, making supplementation critical.
Reference: Allen, L. H. (2009). How common is vitamin B-12 deficiency? The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition https://ajcn.nutrition.org/article/S0002-9165(23)23998-2/fulltext
B12 deficiency can cause irreversible nerve damage if left untreated. Symptoms like tingling in the hands and feet, balance issues, and cognitive decline often develop gradually, making early supplementation critical.
.
Unlike fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), B12 dissolves in water and excess amounts are simply excreted in urine. This means high doses don’t build up to toxic levels like some other vitamins can.
Health authorities, including the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), have found no evidence of toxicity even at very high doses (e.g., 5000 mcg daily). See publication here
Some people report mild effects when taking high doses, such as:
For most people, high doses of B12 offer a safety net against deficiency, support cognitive health, and boost energy—without any real downside. If you’re vegan, over 50, have digestive issues, or take medications that affect B12 absorption, supplementing with a high dose may be one of the best things you can do for your long-term health.
Several studies have examined the link between B12 and cognitive function. Here are five key pieces of research:
Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Cognitive Impairment
A systematic review found 43 studies linking low B12 levels to cognitive impairment and dementia, highlighting the strong correlation between deficiency and brain health decline.
📚 Reference: O’Leary, F., & Samman, S. (2010). Vitamin B12 and cognition: A review of the evidence. National Institutes of Health (NIH)
(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22221769/?utm_source=chatgpt.com)
Vitamin B12 and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk
Research from the American Academy of Neurology suggests that adequate B12 levels may help protect against Alzheimer’s disease, contributing to lower levels of brain shrinkage in older adults.
📚 Reference: International Alzheimer’s Conference Findings (2013). American Academy of Neurology (AAN)
(https://www.aan.com/PressRoom/Home/PressRelease/872?utm_source=chatgpt.com)
B12 Deficiency in Dementia Patients
A study in The Journal of Neuropsychiatry found that 29-47% of dementia patients have low B12 levels, reinforcing its role in cognitive function.
📚 Reference: Kountouras, J., et al. (2007). The role of vitamin B12 in cognitive decline and dementia. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry
(https://psychiatryonline.org/doi/full/10.1176/jnp.12.3.389?utm_source=chatgpt.com)
Vitamin B12, Homocysteine, and Cognitive Decline
Elevated homocysteine levels—often caused by low B12—are associated with a higher risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
📚 Reference: Smith, A. D., et al. (2010). Homocysteine and brain atrophy in cognitively impaired elderly people. British Journal of Nutrition (Cambridge University Press)
(https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/british-journal-of-nutrition/article/vitamin-b12-status-cognitive-decline-and-dementia-a-systematic-review-of-prospective-cohort-studies/51BBCC9458B5C1F64A03E3F75C070FEA?utm_source=chatgpt.com)
Vitamin B12, B6, and Folate Supplementation and Brain Health
Research suggests that high-dose B12, B6, and folate supplementation may slow neurodegenerative processes and reduce homocysteine levels linked to dementia risk.
📚 Reference: Clarke, R., et al. (2013). B Vitamins and the Prevention of Cognitive Decline. Alzheimer’s Research Forum
(https://www.alzforum.org/news/research-news/too-much-vitamin-b12-health-hazard?utm_source=chatgpt.com)
NeuroBright is designed with optimal B-vitamin levels to support cognition, energy, and neurological function. Our formula includes:
This combination is scientifically backed to enhance cognitive performance and maintain neurological health. If you’re looking for a comprehensive, high-dose B-vitamin supplement designed specifically for brain function and longevity, NeuroBright provides the right balance—without the risks of toxicity.
General Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or before making any changes to your diet, supplement regimen, or lifestyle. We cannot be held responsible for any decisions made based on the information presented here.
To receive our Newsletter of Research into Vitamins that may help Memory, reduce Tiredness and reduce the chances of Dementia, Alzheimer’s and Cognitive decline please leave your email address below.
In the previous blog, we explored the vitamins and minerals that directly participate in ATP production, which is the process
Feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep? Struggling with afternoon crashes, brain fog, or low stamina during workouts? While
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and to analyse our website traffic. We will not share any of your personal details.