The Vitamins and Minerals That Support Energy Indirectly
In the previous blog, we explored the vitamins and minerals that directly participate in ATP production, which is the process
Feeling tired even after a full night’s sleep? Struggling with afternoon crashes, brain fog, or low stamina during workouts?
While caffeine can mask tiredness, it does not fix the root cause. Real energy comes from inside your cells, specifically from a molecule called ATP. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is your body’s true energy currency. Every thought, muscle movement, heartbeat, and repair process depends on it. So, when your body does not have the nutrients required to make ATP efficiently, fatigue becomes a daily companion.
Understanding the vitamins and minerals that directly support ATP synthesis, and how they help your body feel energised, focused, and steady throughout the day is quite crucial.
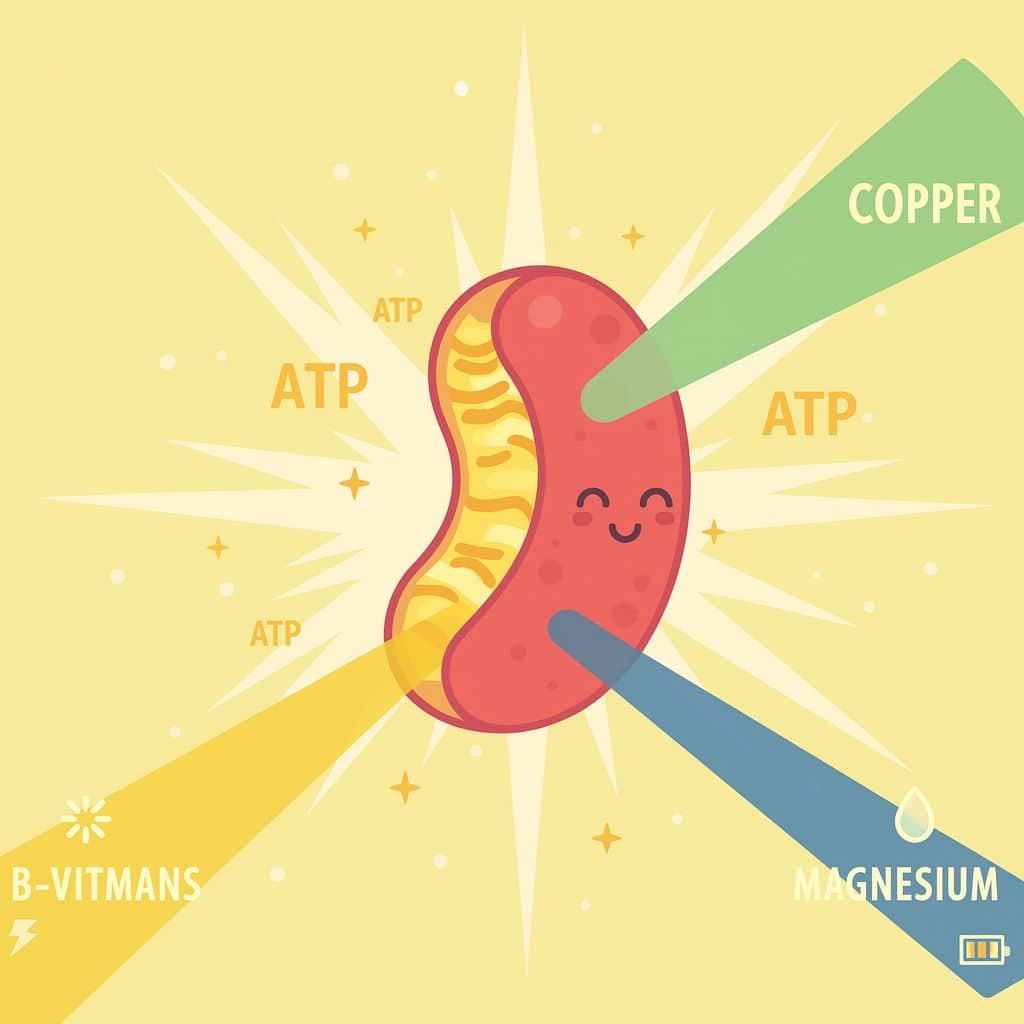
ATP is produced inside mitochondria (the powerhouse of your cell). The more ATP your cells can produce, the better your body performs:
When ATP production dips, you feel it instantly: low energy, irritability, reduced stamina, and mental sluggishness.
The good news? Your body can produce ATP extremely efficiently… as long as it has the right nutrients.
Vitamins and minerals such as B-vitamins, Copper, and Magnesium, actively participate in ATP synthesis inside the mitochondria.
B-vitamins act like spark plugs in your metabolic engine. Without them, ATP production slows no matter how well you eat or sleep.
Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
Converts carbohydrates into usable energy. Essential for turning pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, the key entry molecule for the Krebs cycle (energy production).
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Creates FAD and FMN, two coenzymes that drive the electron transport chain, which is the final and most efficient stage of ATP production.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Forms NAD/NADH, one of the most important molecules in energy metabolism. NADH donates electrons that ultimately generate ATP.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
A core component of Coenzyme A, which feeds into the Krebs cycle and helps break down fats, proteins, and carbs for energy.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Helps release glycogen (stored sugar), particularly during exercise or stress. Supports amino acid metabolism, vital for muscle performance.
Vitamin B12 (Methylcobalamin)
Crucial for red blood cell formation, which directly affects oxygen delivery. Better oxygen = more ATP.
Copper is a key component of cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme in Complex IV of the electron transport chain; one of the final steps where your cells actually generate ATP.
Copper helps to:
When copper is low, ATP output drops, oxygen use becomes less efficient, and fatigue becomes more noticeable.
Magnesium is an important mineral for energy. It matters because the ATP must bind to magnesium to be biologically active. So, your body does not use “ATP”; it uses Mg-ATP.
Magnesium is required for:
Poor magnesium status can contribute to tiredness, heavy limbs, and frequent muscle fatigue.
These simple habits help your mitochondria stay efficient and resilient.
Energy is not something you “get” from a drink or a stimulant; it is something your cells create using ATP.
Vitamins and minerals are the raw materials and co-factors that make that possible.
Supporting your body with the right nutrients means you will have a higher stamina, better focus, smoother workouts, more stable energy throughout the day, and less fatigue and quicker recovery.
To receive our Newsletter of Research into Vitamins that may help Memory, reduce Tiredness and reduce the chances of Dementia, Alzheimer’s and Cognitive decline please leave your email address below.
In the previous blog, we explored the vitamins and minerals that directly participate in ATP production, which is the process
The brain and body share more in common than we often realise, especially when it comes to the minerals that
We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience and to analyse our website traffic. We will not share any of your personal details.